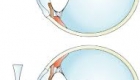
Astigmatism is a common type of refractive error. It is a condition in which the eye does not focus light
How does astigmatism occur?
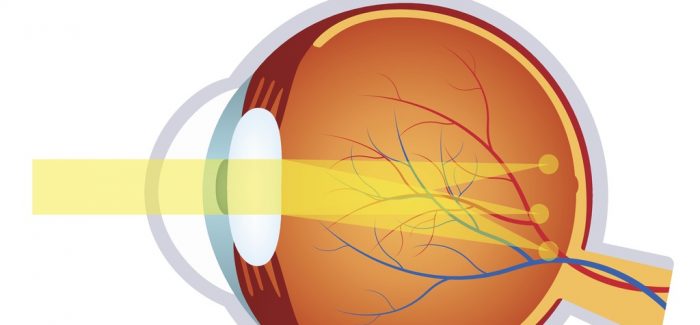
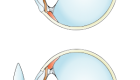
Astigmatism occurs when light is bent differently depending on where it strikes the cornea and passes through the eyeball. The cornea of a normal eye is curved like a basketball, with the same degree of roundness in all areas. An eye with astigmatism has a cornea that is curved more like a football, with some areas that are steeper or more rounded than others. This can cause images to appear blurry and stretched out.
Who is at risk for astigmatism?
Astigmatism can affect both children and adults. Some patients with slight astigmatism will not notice much change in their vision. It is important to have eye examinations at regular intervals in order to detect any astigmatism early on for children.
What are the signs and symptoms of astigmatism?
Signs and symptoms include:
- Headaches
- Eyestrain
- Squinting
- Distorted or blurred vision at all distances
- Difficulty driving at night
If you experience any of these symptoms, visit your eye care professional. If you wear glasses or contact lenses and still have these issues, a new prescription might be needed.
How is astigmatism diagnosed?
Astigmatism is usually found during a comprehensive dilated eye exam.
Can you have astigmatism and not know it?
It is possible to have mild astigmatism and not know about it. This is especially true for children, who are not aware of their vision being other than normal. Some adults may also have mild astigmatism without any symptoms. It's important to have comprehensive dilated eye exams to make sure you are seeing your best.
Treatment
Astigmatism can be corrected with
- Eyeglasses
- Contact lenses
- Surgery