Cataract
Inside our eyes, we have a natural lens. The lens bends (refracts) light rays that come into the eye to help us see. The lens should be clear
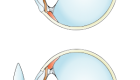
If you have a cataract, your lens has become cloudy, like the bottom lens in the illustration. It is like looking through a foggy or dusty car windshield. Things look blurry, hazy or less colorful with a cataract.
There are different types of cataracts. They include:
- Age-related. These form as you get older. Though there are other risk factors for cataracts, aging is the most common cause. This is due to normal eye changes that happen after around age 40. That is when normal proteins in the lens start to break down. This is what causes the lens to get cloudy.
- Congenital. This is what doctors call it when babies are born with cataracts. They may be caused by infection, injury, or poor development in the womb. Or, they can form in childhood.
- Secondary. These happen as a result of other medical conditions, like diabetes. They can also result from being around toxic substances, ultraviolet light, or radiation, or from taking medicines such as corticosteroids or diuretics.
- Traumatic. These form after an injury to the eye.
Other things that can raise your chances of getting cataracts include cigarette smoke, air pollution, and heavy drinking.
Cataract symptom progression
Here are some vision changes you may notice if you have a cataract:
- Having blurry vision
- Seeing double (when you see two images instead of one)
- Being extra sensitive to light
- Having trouble seeing well at night, or needing more light when you read
- Seeing bright colors as faded or yellow instead
Who Is at Risk for Cataracts?
Besides aging, other cataract risk factors include:
- having parents, brothers, sisters, or other family members who have cataracts
- having certain medical problems, such as diabetes
- having had an eye injury, eye surgery, or radiation treatments on your upper body
- having spent a lot of time in the sun, especially without sunglasses that protect your eyes from damaging ultraviolet (UV) rays
If you have any of these risk factors for cataract, you should schedule an appointment with your ophthalmologist.
Your ophthalmologist will examine and test your eyes to make a cataract diagnosis. This comprehensive eye exam will include dilation. This means eye drops will widen your pupils.
Cataract Treatment
Do not use eye drops or other treatments that claim to dissolve or remove cataracts. There is no proven way to dissolve cataracts with eye drops. Surgery is the only way to remove cataracts.
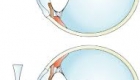
During cataract surgery, your eye surgeon will remove your eye’s cloudy natural lens. Then he or she will replace it with an artificial lens. This new lens is called an intraocular lens (or IOL).
Before surgery:
Your ophthalmologist will measure your eye to set the proper focusing power for your IOL. Also, you will be asked about any medicines you take. You might be asked not to take some of these medicines before surgery.
Phacoemulsification, the eye surgeon creates a small incision in the side of the cornea special pen-shaped probe is inserted through that opening to apply sound waves (ultrasound) to break up the cloudy center of the lens. Then the broken-up pieces of lens are suctioned out of the eye. An artificial intraocular lens (IOL) is implanted to replace the cloudy natural lens. The side walls of the corneal incision will be filled with a special liquid and self-seal after surgery, so most commonly stitches are not needed.
After the operation, a patch may be placed over your eye. You will rest for a while. Your medical team will watch for any problems, such as bleeding. Most people who have cataract surgery can go home the same day. You will need someone to drive you home.
Problems after surgery are rare, but they can occur. These problems can include infection, bleeding, inflammation (pain, redness, swelling), loss of vision, double vision, and high or low eye pressure. With prompt medical attention, these problems can usually be treated successfully.
Sometimes the eye tissue that encloses the IOL becomes cloudy and may blur your vision. This condition is called an after-cataract. An after-cataract can develop months or years after cataract surgery.
An after-cataract is treated with a laser. Your doctor uses a laser to make a tiny hole in the eye tissue behind the lens to let light pass through. This outpatient procedure is called a YAG laser capsulotomy. It is painless and rarely results in increased eye pressure or other eye problems. As a precaution, your doctor may give you eyedrops to lower your eye pressure before or after the procedure.
What are the risks of cataract surgery?
Like any surgery, cataract surgery carries risks of problems or complications. Here are some of those risks:
- Eye infection.
- Bleeding in the eye.
- Ongoing swelling of the front of the eye or inside of the eye.
- Swelling of the retina (the nerve layer at the back of your eye).
- Detached retina (when the retina lifts up from the back of the eye).
- Damage to other parts of your eye.
- Pain that does not get better with over-the-counter medicine.
- Vision loss.
- The IOL implant may become dislocated, moving out of position.
Your ophthalmologist will talk with you about the risks and benefits of cataract surgery