Cross linking
Surgical Therapy
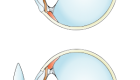
Corneal collagen cross-linking is a technique which uses UV light and a photosensitizer to strengthen chemical bonds in the cornea. The goal of the treatment is to halt progressive and irregular changes in corneal shape known as ectasia. These ectatic changes are typically marked by corneal thinning and an increase in the anterior and/or posterior curvatures of the cornea, and often lead to high levels of myopia and astigmatism. The most common form of ectasia is keratoconus and less often ectasia is seen after laser vision correction such as LASIK.
Indications
The primary purpose of crosslinking is to halt the progression of ectasia. Likewise, the best candidate for this therapy is an individual with a progressive ectatic disease of the cornea. The most common indication is keratoconus. Other diseases that may be candidates include Pellucid Marginal Degeneration, Terrien Marginal Degeneration, and post-refractive surgery (such as LASIK or Radial Keratotomy) ectasia. There currently are no definitive criteria for progression, but parameters to consider are change in refraction (including astigmatism), uncorrected visual acuity, best corrected visual acuity, and corneal shape (topography and tomography).
Contraindications
- Corneal thickness of less than 400 microns is a contraindication to the standard treatment protocol
- Prior herpectic infection is a contraindication because it may result in viral reactivation
- Concurrent infection
- Severe corneal scarring or opacification
- History of poor epithelial wound healing
- Severe ocular surface disease (ex. dry eye)
- Autoimmune disorders
Surgical Technique
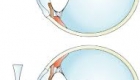
The primary goal of the first stage of therapy is to allow riboflavin to diffuse into the cornea. While there are several variations on the techniques used to accomplish this, all entail either removing or weakening the epithelial barrier of the cornea. In all instances the patient is first given anesthetic drops. Some ophthalmologists will also give preoperative antibiotics. A lid speculum is placed. After disrupting the epithelium, drops of riboflavin 0.1% (vitamin B2) are given at intervals of 1-5 minutes for 15 - 30 minutes, or until riboflavin can been seen in the anterior chamber of the eye by use of the blue filter on slit lamp examination.
After adequate riboflavin absorption, the patient is positioned with the UV light (typically 365-370um) at a small distance (1-5cm) from the corneal apex for 30 minutes.
Following irradiation, antibiotic drops are given and a bandage contact lens is typically placed.